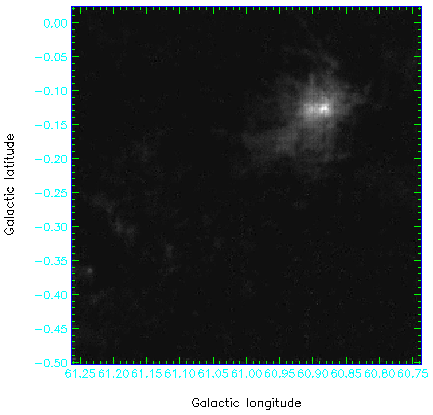
map.sdf. Do draw axes and a border, but do not draw a title or a grid. The default cut parameters
for mode=scale include all the data.
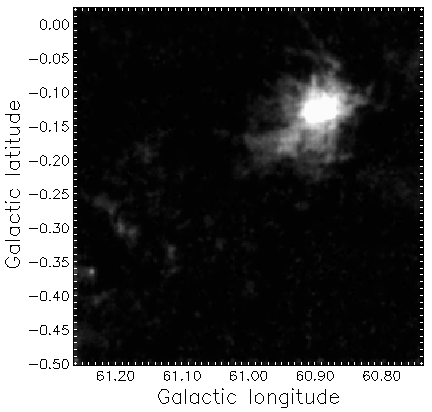
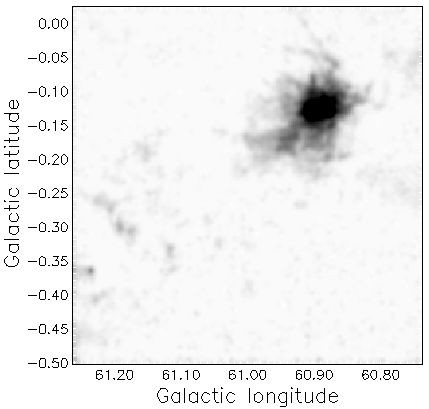
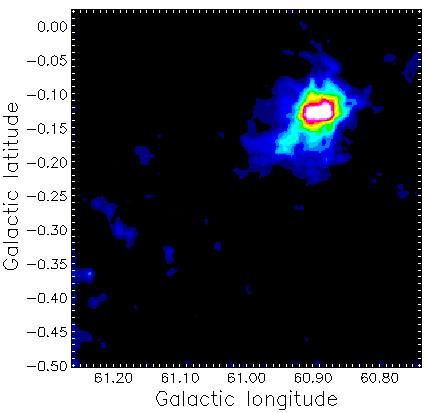
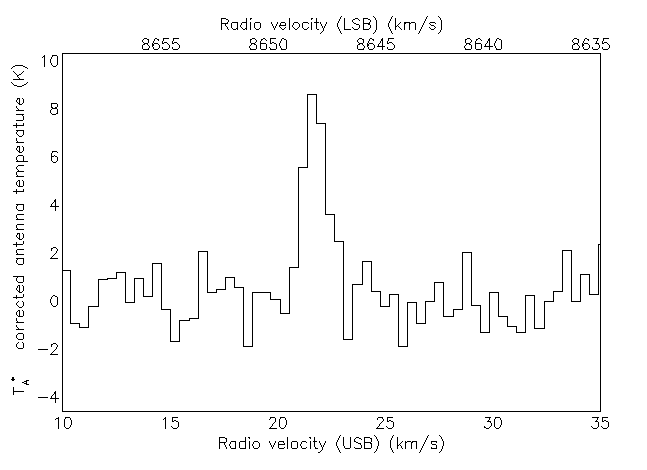
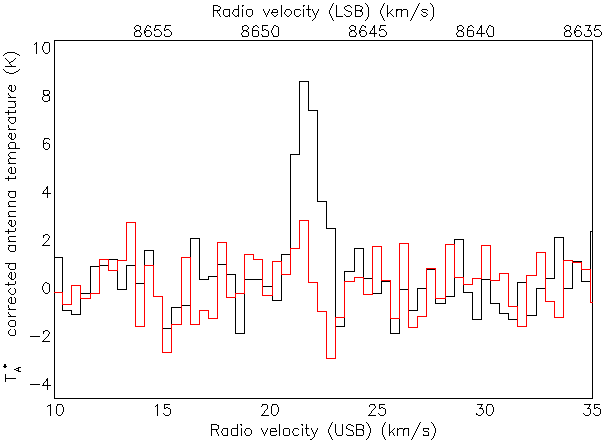
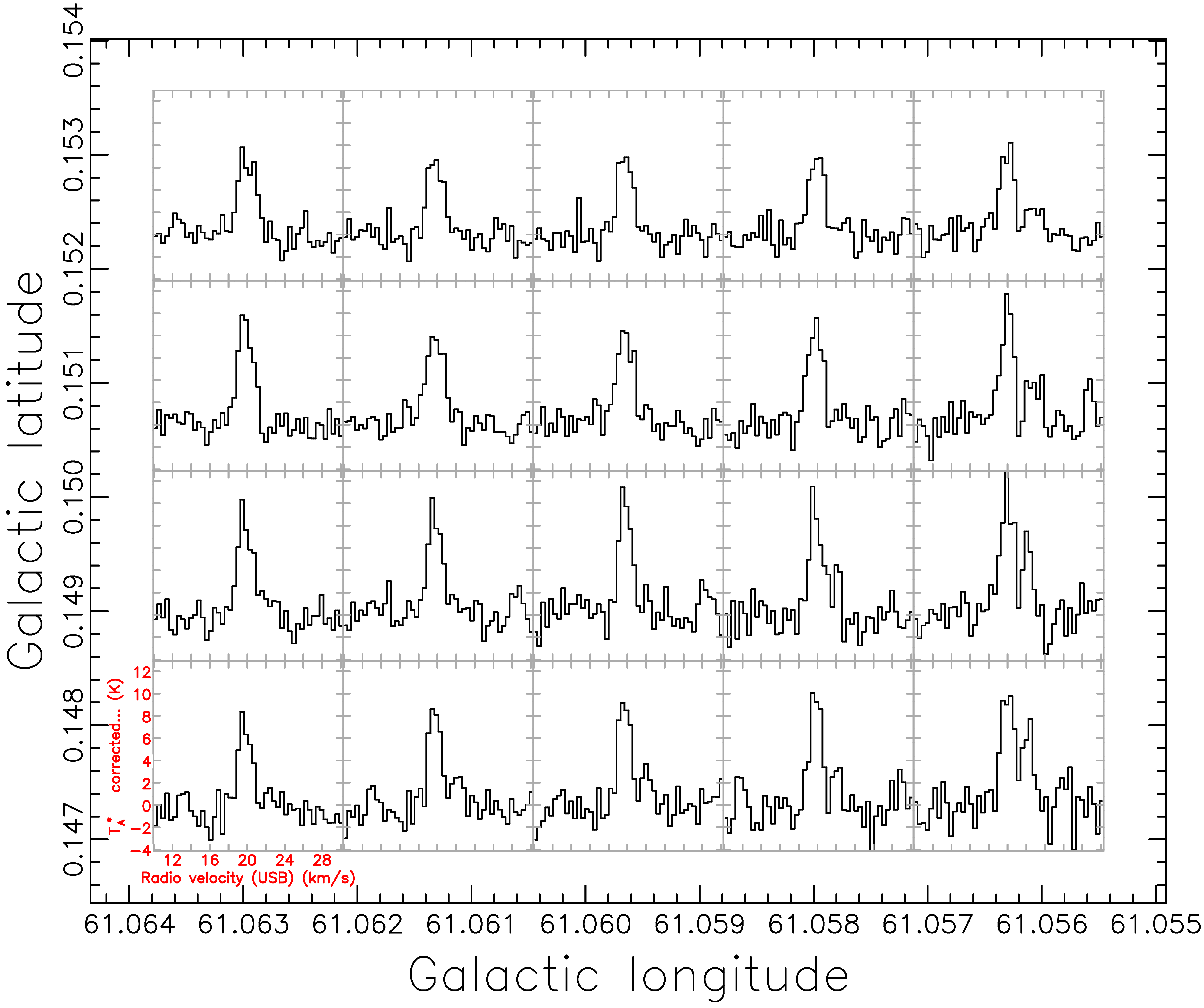
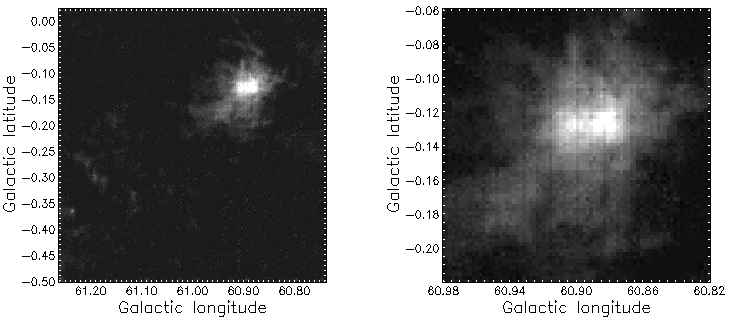
Depending on your default settings you may get a map like the one below.
Below is a copy of the style file (style.dat) used to make Figure F.2.
$STARLINK_DIR//bin/kappa/ directory.
You can create your own colour scheme using the Kappa routine lutedit. See the Kappa manual for more details.
lut option.
lut=$STARLINK_DIR/bin/kappa/random3_lut